# Controllers
A controller is an object whose properties are functions. These functions will be called by the OpenAPI Enforcer Middleware according to the x-controller and x-operation attributes you specify in your OpenAPI document. When these functions are called, they will receive the request, response, and next function as parameters.
You can define your controller objects one of two ways:
As an
object.As a
functionthat returns an object.
# Controller via an Object
Define the object, naming the properties the same as those listed as the x-operation properties in your OpenAPI document.
module.exports = {
addPerson: async function (req, res, next) {
await savePersonToDatabase(req.body)
res.sendStatus(201)
},
getPerson: async function (req, res, next) {
const person = await getPersonById(req.params.personId)
if (person) {
res.send(person)
} else {
res.sendStatus(404)
}
}
}
# Controller via a Function
When creating a controller via a function, the function must return an object that looks like a controller object. The advantage of this method is that it allows for dependency injection.
module.exports = function () {
return {
addPerson: async function (req, res, next) {
await savePersonToDatabase(req.body)
res.sendStatus(201)
},
getPerson: async function (req, res, next) {
const person = await getPersonById(req.params.personId)
if (person) {
res.send(person)
} else {
res.sendStatus(404)
}
}
}
}
# Dependency Injection
Dependency injection is when you pass dependencies (database connections, data, functionality, etc.) into a function so that it can use the dependencies to accomplish its task.
For example, if you have a controller that requires a connection to the database to operate, you may want to pass that dependency in. This improves the testability of your code.
Accomplishing dependency injection with the OpenAPI Enforcer middleware is a two step process:
Define a controller via a function and add parameters to the function signature:
module.exports = function (databaseConnection, someData) { const controller = {} controller.addPerson = async function (req, res, next) { const { id, name } = req.body const rows = await databaseConnection.query('INSERT INTO people (id, name) VALUES ($1, $2)', [ id, name ]) res.send(rows) } return controller }When telling the OpenAPI Enforcer Middleware where to find the controller, also specify the parameters to pass in:
const EnforcerMiddleware = require('openapi-enforcer-middleware') const express = require('express') const app = express() const enforcer = EnforcerMiddleware('/path/to/openapi-definition.yml') const databaseConnection = getDatabaseConnection() const someData = { ... } // pass in dependencies enforcer.controllers('/path/to/controllers-dir', databaseConnection, someData) app.use(enforcer.middleware()) app.listen(3000)
# Referencing Controllers
You know how to define a controller. Here we cover how you can set up the OpenAPI Enforcer middleware can call it.
# Controllers in Files
Placing each unique controller in its own file is the recommended method. It simplifies code and makes it easily testable.
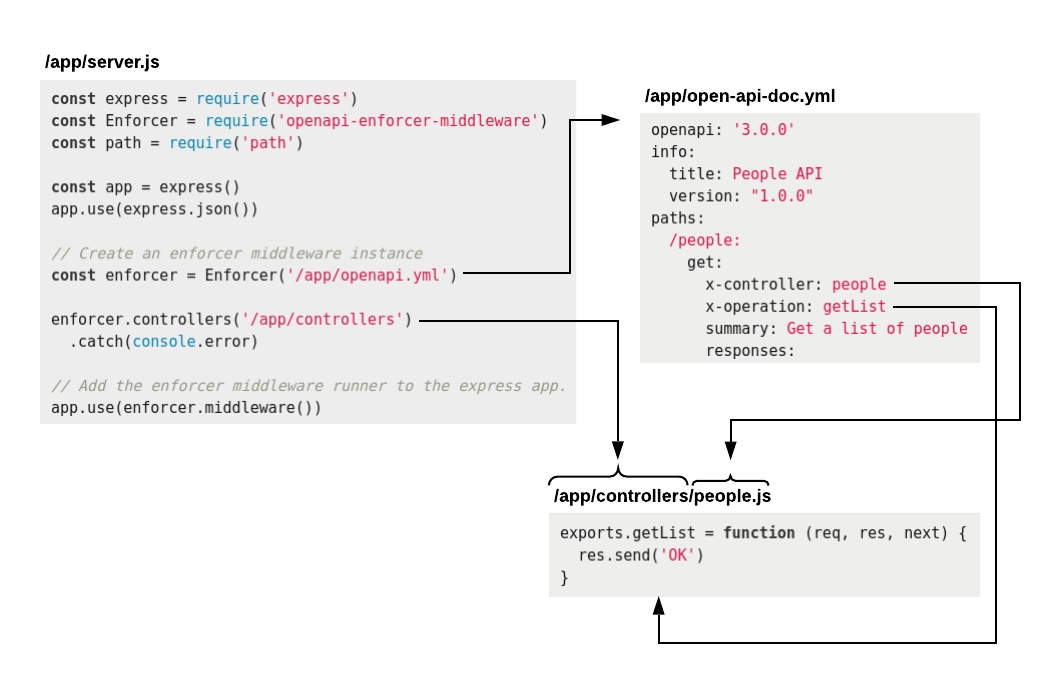
Choose a directory where you'll put your controller files.
Create files with the same names as the
x-controllerproperty in your OpenAPI document.For example, you will need a file named
people.jsif you have an OpenAPI document with anx-controllerset topeoplepaths: /people: get: x-controller: people x-operation: getList ...Export your controller object or function from each file, defining the properties that match the operations.
people.js
exports.getList = async function (req, res, next) { const list = await getAllPeople() res.send(list) }
# Inline Controllers
Inline controllers are defined as an object whose properties are the x-controller names and its values are a controller object. Below is a section of an OpenAPI document and a section of how you would set up your server to use inline controllers.
OpenAPI Document
paths:
/people/{id}:
get:
x-controller: people
x-operation: getPerson
...
Server File
// Create a controllers map
const controllersMap = {
people: { // associates to x-controller: people
// associates to x-operation: getPerson
getPerson: async function (req, res, next) {
const person = await getPersonById(req.params.id)
if (person) {
res.send(person)
} else {
res.sendStatus(404)
}
}
}
}
// Add controllers
enforcer.controllers(controllersMap)
.catch(console.error)
// Add the enforcer middleware runner to the express app.
app.use(enforcer.middleware())